Deploy with Terraform
Use Terraform in a Codefresh pipeline with Docker
Terraform is a platform for Infrastructure as Code. It allows you to describe your cloud infrastructure in a declarative manner.
You can use Terraform to deploy to Kubernetes or any other supported cloud platform. Because Terraform itself is already offered in a Docker container, it is very easy to run Terraform in a Codefresh pipeline.
NOTE
This page explains how to run Terraform inside a Codefresh pipeline. If you want to use Terraform to manage Codefresh itself see the Terraform provider.
The example Terraform project
You can see the example project at https://github.com/codefresh-contrib/terraform-sample-app. The repository contains a simple Terraform definition that creates a VM on Google cloud.
You can play with it locally after installing the terraform executable.
Prerequisites
You need to create a Codefresh account and a Google account first. Then you need to create a Service account Key which will allow terraform to communicate with Google cloud.
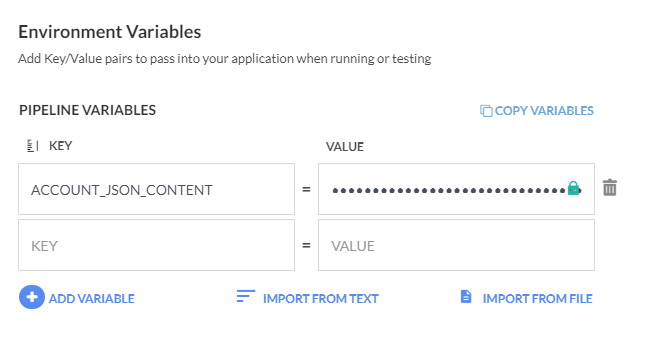
Add your service account json as a pipeline variable called ACCOUNT_JSON_CONTENT. The content of this variable will be used
in order to authenticate to Google cloud.
Create a CI/CD pipeline for Terraform
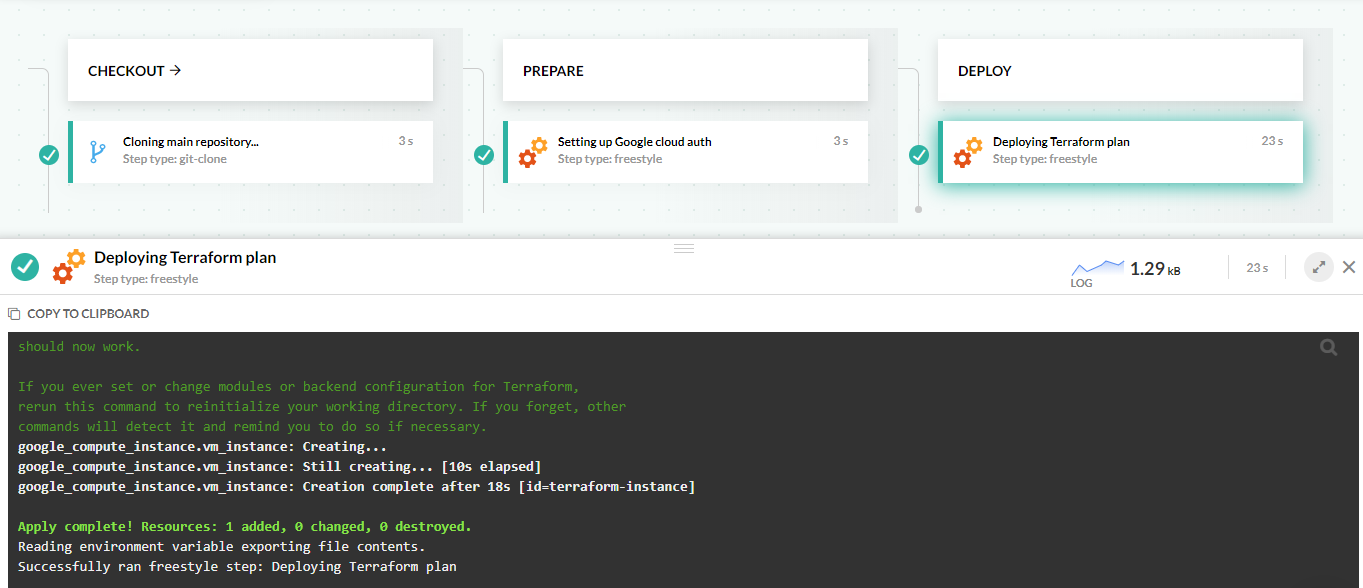
Here is the whole pipeline:
codefresh.yml
version: '1.0'
stages:
- checkout
- prepare
- deploy
steps:
main_clone:
title: Cloning main repository...
stage: checkout
type: git-clone
repo: 'codefresh-contrib/terraform-sample-app'
revision: master
git: github
SetupAuth:
image: alpine:3.9
title: Setting up Google cloud auth
stage: prepare
commands:
- echo $ACCOUNT_JSON_CONTENT > /codefresh/volume/account.json
- cf_export GOOGLE_CLOUD_KEYFILE_JSON=/codefresh/volume/account.json
DeployWithTerraform:
image: hashicorp/terraform:0.12.0
title: Deploying Terraform plan
stage: deploy
commands:
- terraform init
- terraform apply -auto-approve This pipeline does the following:
- Clones the source code through a Git clone step.
- Creates a pipeline variable with the path of the Google service account by running cf_export.
- Creates the VM on Google cloud by running
terraform init/apply.
NOTE
For simplicity, we auto-approve the Terraform plan in the example pipeline. In a production pipeline, you would instead use an approval step to inspect the plan before actually applying it.
The pipeline needs a single environment variable that holds the content of the service account.
Run the pipeline and see your deployment succeed.
Note that in a production pipeline you should also handle the Terraform state in a proper manner. The example provided is using a file for state storage which is not appropriate when using Terraform in a team environment. Instead you should use one of the storage backends that support High Availability and Locking.
Handling Pull requests
You can easily use the same pipeline or a different one for pull requests. In this case replace the terraform apply command with terraform plan. Even better, you can add an approval step to allow humans to inspect the pipeline first.
Related articles
CD pipeline examples
Codefresh YAML for pipeline definitions
Creating pipelines
How Codefresh pipelines work