Run unit tests
Running unit tests in Codefresh pipelines
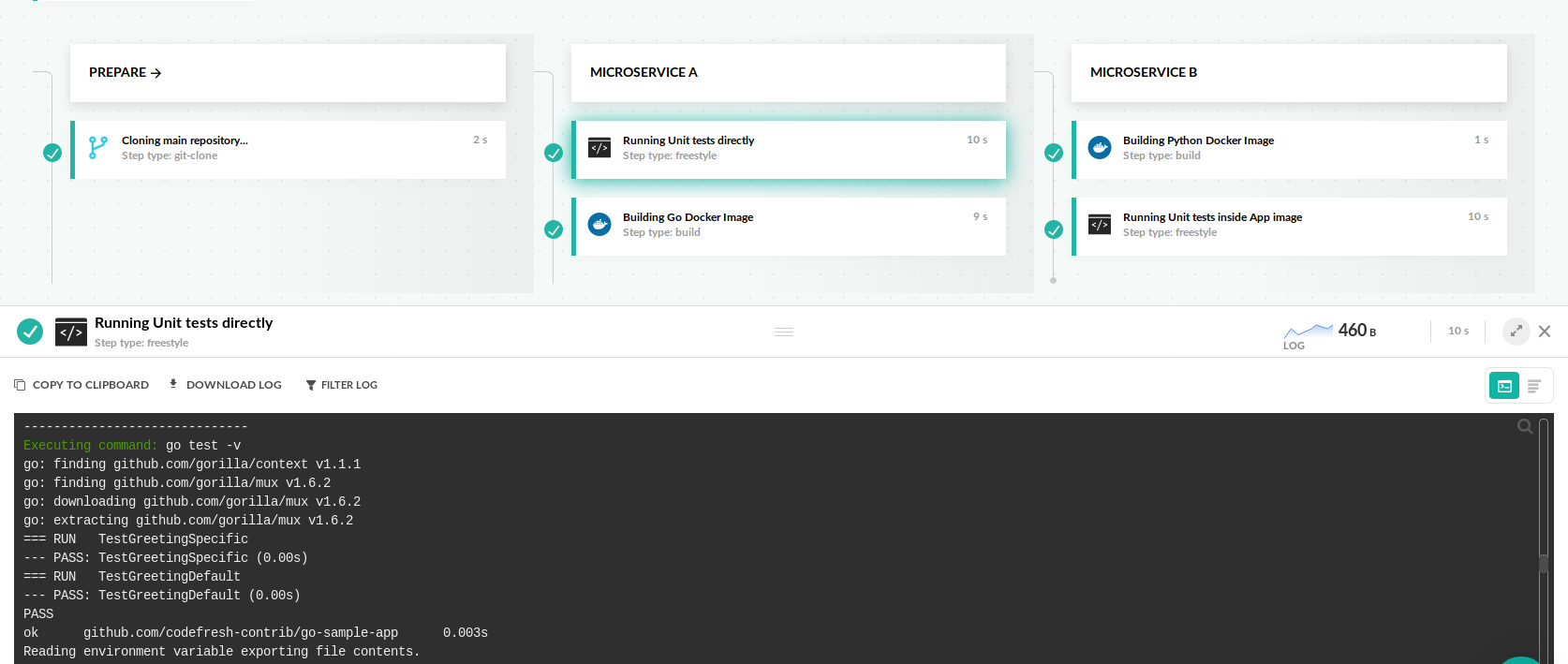
As explained in unit tests, Codefresh supports several ways of running unit tests. The most common scenarios use an existing Docker Hub image (common with compiled languages such as Java and Go), or the application image itself (common with languages such as JavaScript/Python/Ruby/PHP).
In this example, we will see both ways using two different applications in a single pipeline.
In the first case, we run unit tests before creating the application docker image. In the second case, we run the unit tests inside the application Docker image.
Example Python/Go project
You can see the example project at https://github.com/codefreshdemo/cf-example-unit-test. The repository contains two applications (Python and Go) with their respective unit tests.
You can play with it locally by using Docker commands to package the applications.
Create a pipeline with unit tests
Here is the whole pipeline:
codefresh.yml
version: '1.0'
stages:
- prepare
- 'Microservice A'
- 'Microservice B'
steps:
main_clone:
title: Cloning main repository...
type: git-clone
repo: 'codefreshdemo/cf-example-unit-test'
revision: 'master'
git: github
stage: prepare
run_my_tests_before_build:
title: Running Unit tests directly
stage: 'Microservice A'
image: golang:1.12
working_directory: './golang-app-A'
commands:
- go test -v
build_after_my_tests:
title: Building Go Docker Image
type: build
stage: 'Microservice A'
image_name: my-go-image
working_directory: './golang-app-A'
tag: 'master'
dockerfile: Dockerfile
build_before_my_tests:
title: Building Python Docker Image
type: build
stage: 'Microservice B'
image_name: my-python-image
working_directory: './python-app-B'
tag: 'master'
dockerfile: Dockerfile
run_my_tests_inside_image:
title: Running Unit tests inside App image
stage: 'Microservice B'
image: ${{build_before_my_tests}}
working_directory: '/app'
commands:
- python setup.py test This pipeline does the following:
- Clones the source code through a Git clone step.
- Runs unit test for the GO application using the Dockerhub image
golang:1.12. - Builds the Docker image for the Go application through a build step.
- Builds the Docker image for the Python application.
- Runs unit tests for the Python application using as runtime context the application image that was just created.
In the second case, the tests run in the context of build_before_my_tests which is the name of the step that creates the Docker image for Python. Read more about context variables.
We generally recommend the first approach, so that your production Docker image does not contain any unit testing libraries or frameworks, but there is no right or wrong choice regarding the way you run unit tests.
Related articles
CI pipeline examples
Unit tests
Integration test example
Service containers in pipelines
Steps in pipelines