Launch-Composition step
Create a test environment with its dependencies in Codefresh infrastructure
The Launch Composition step provides the ability to launch long term running environments that can live outside the context of a running pipeline. You can use this step to automate your test environment creation through a codefresh.yml file instead of manually launching an environment from the UI.
NOTE
launch-compositioncreates a permanent test environment that keeps running even after a pipeline has finished. If you just want temporary test environments that run only while a pipeline is running, see service containers and the documentation page for integration tests.
Usage
ui defined composition
step_name:
title: Step Title
type: launch-composition
composition: 'ui_defined_composition_name'
environment_name: 'environment name'
on_success:
...
on_fail:
...
on_finish:
...inline composition
step_name:
type: launch-composition
composition:
version: '2'
services:
app:
image: owner/app:latest
db:
image: mongo
environment_name: 'environment name'
on_success:
...
on_fail:
...
on_finish:
...
retry:
... from file composition
step_name:
type: launch-composition
working_directory: $
composition: './path/to/docker-compose.yaml'
environment_name: 'environment name'
on_success:
...
on_fail:
...
on_finish:
...Fields
| Field | Description | Required/Optional/Default |
|---|---|---|
title |
The free-text display name of the step. | Optional |
description |
A basic, free-text description of the step. | Optional |
stage |
Parent group of this step. See using stages for more information. | Optional |
working_directory |
The directory in which to search for the composition file. It can be an explicit path in the container’s file system, or a variable that references another step. The default is ${{main_clone}}. |
Default |
composition |
The composition you want to run. It can be an inline YAML definition, a path to a composition file on the file system, or the logical name of a composition stored in the Codefresh system. | Required |
environment_name |
The environment name that will be given. In case a previous environment exists with the same name, it will first be terminated. The default value will the be the name/path provided in the ‘composition’ field. | Default |
composition_variables |
A set of environment variables to substitute in the composition. | Optional |
timeout |
The maximum duration permitted to complete step execution in seconds (s), minutes (m), or hours (h), after which to automatically terminate step execution. For example, timeout: 1.5h. The timeout supports integers and floating numbers, and can be set to a maximum of 2147483647ms (approximately 24.8 days). If defined and set to either 0s/m/h or null, the timeout is ignored and step execution is not terminated.See Add a timeout to terminate step execution. |
Optional |
fail_fast |
Determines pipeline execution behavior in case of step failure.
|
Optional |
strict_fail_fast |
Specifies how to report the Build status when fail_fast is set to false.NOTE: Requires Runner chart upgrade to v6.3.9 or higher. You can set the Build status reporting behavior at the root-level or at the step-level for the pipeline.
NOTES: strict_fail_fast does not impact the Build status reported for parallel steps with fail_fast enabled. Even if a child step fails, the parallel step itself is considered successful. See also Handling error conditions in a pipeline. |
Optional |
when |
Define a set of conditions which need to be satisfied in order to execute this step. You can find more information in the conditional execution of steps article. |
Optional |
on_success, on_fail and on_finish |
Define operations to perform upon step completion using a set of predefined post-step operations. | Optional |
| entry_point | The name of main service | Optional |
retry |
Define retry behavior as described in retrying a step. | Optional |
Add a timeout to terminate step execution
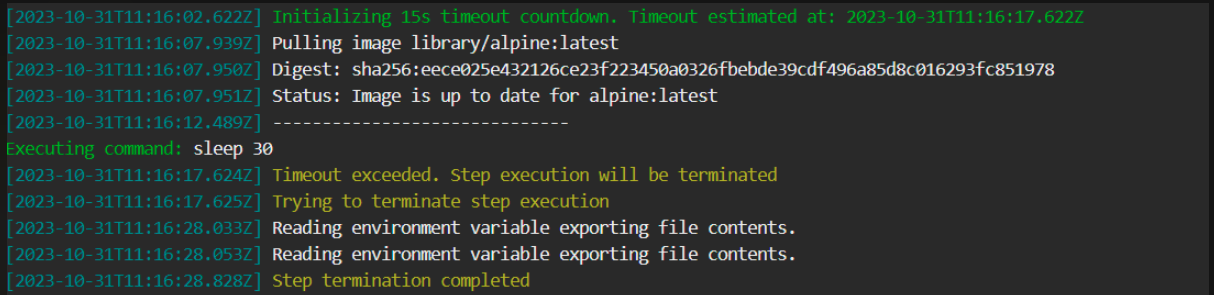
To prevent steps from running beyond a specific duration if so required, you can add the timeout flag to the step.
When defined:
- The
timeoutis activated at the beginning of the step, before the step pulls images. - When the step’s execution duration exceeds the duration defined for the
timeout, the step is automatically terminated.
NOTE
To define timeouts for parallel steps, see Adding timeouts for parallel steps.
Here’s an example of the timeout field in the step:
ui defined composition
step_name:
title: Step Title
type: launch-composition
composition: 'ui_defined_composition_name'
environment_name: 'environment name'
timeout: 45m
on_success:
...
on_fail:
...
on_finish:
...inline composition
step_name:
type: launch-composition
timeout: 45m
composition:
version: '2'
services:
app:
image: owner/app:latest
db:
image: mongo
environment_name: 'environment name'
on_success:
...
on_fail:
...
on_finish:
...
retry:
... from file composition
step_name:
type: launch-composition
working_directory: $
composition: './path/to/docker-compose.yaml'
environment_name: 'environment name'
timeout: 45m
on_success:
...
on_fail:
...
on_finish:
...Timeout info in logs
Timeout information is displayed in the logs, as in the example below.
Related articles
On-demand environment quick start
Launch Composition example
Integration testing
Service containers in pipelines