Accessing Docker registry from Kubernetes cluster
Allow Kubernetes to pull Docker images from your registry
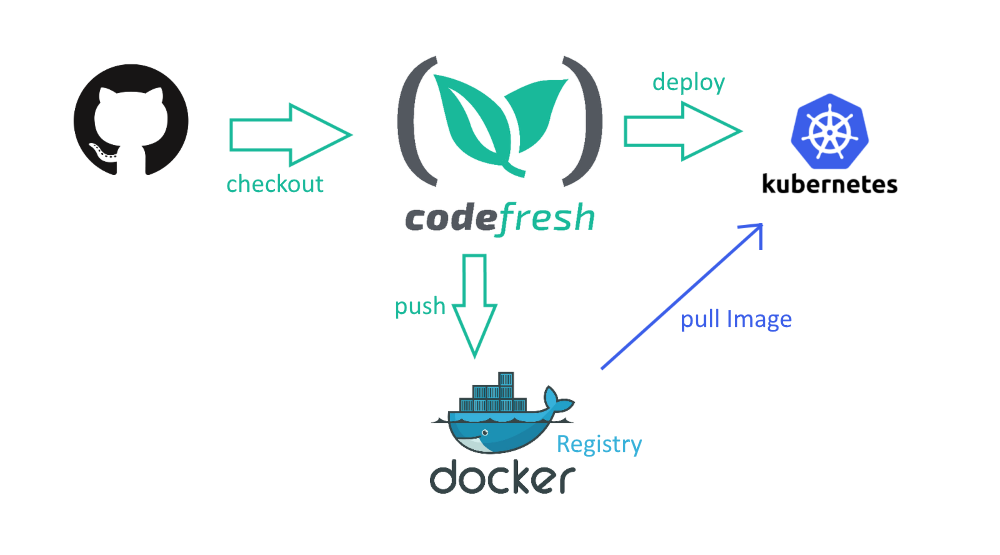
Kubernetes deployments are based on a “pull” approach. When you deploy your application to a Kubernetes cluster, instead of uploading the application itself, as in traditional deployments, Kubernetes pulls the Docker images to its nodes on its own.
If your Docker images are in a public repository such as Docker Hub, Kubernetes can pull them right away. In most cases however your images are in a private Docker registry and Kubernetes must be given explicit access to it.
Use Docker registry secrets to give Kubernetes access to private Docker registries. When there is a deployment, each Kubernetes pod can pull Docker images directly from the target registry.
Giving access to a Docker Registry via the UI
Codefresh allows you to easily create and pull secrets for your cluster.
-
In the Codefresh UI, set up an integration with your Docker registry in Codefresh.
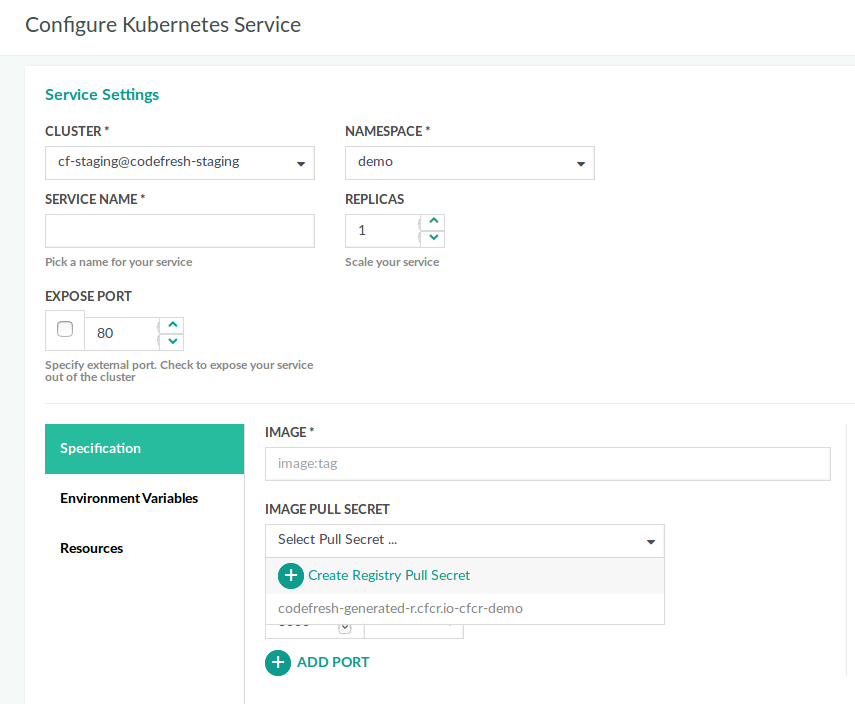
Codefresh can work with any compliant Docker registry either in the cloud or behind the firewall. - To view the Kubernetes dashboard, from the Ops section in the sidebar, select Kubernetes Services.
- Click Add Service.
- Do the following:
- Select your Cluster and Namespace from the respective lists.
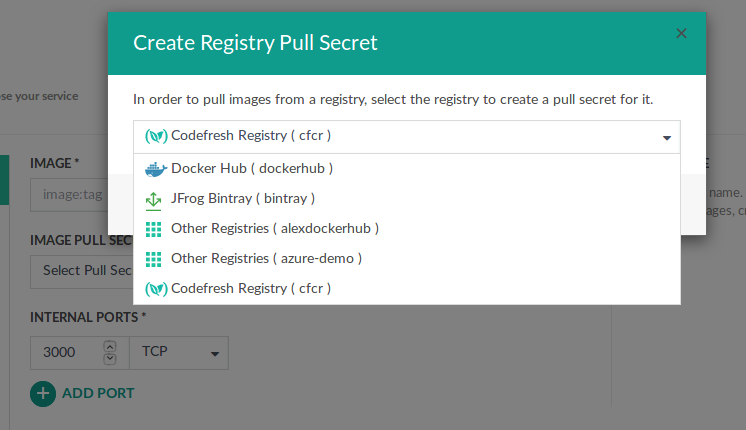
- From the Image Pull Secret dropdown with all the pull secrets for the selected namespace, select Create Registry Pull secret.
- From the list of all the connected Docker registries in Codefresh, select the registry you want. Codefresh automatically creates a secret for you.
NOTE
The secret is created as soon as you select your Docker registry from the dropdown. There is no need to actually deploy anything from this screen for the changes to take effect.
From now on, the cluster in this namespace can deploy Docker images from the selected registry. To apply the changed secret, you don’t really need to finish the deployment. Feel free to close the screen and go to another Codefresh page.
NOTE
Codefresh automatically uses the secret you defined in all deployments that are performed via the UI by dynamically creating the correct manifests for you behind the scenes. If you wish to use your own manifests, you need to include the secret yourself, as explained in the next section.
Giving access to a Docker Registry with kubectl
You can also use the kubectl command directly to give access to a Docker registry.
As this method is not specific to Codefresh, read the official kubernetes documentation.
Creating the Docker registry secret
The credentials depend upon the type of registry you use.
- The Docker server to use is a domain such
gcr.io,azurecr.io - The username is your account username.
- The password is a specific Docker registry password or any other kind of token. You need to check the documentation of your registry provider for the exact details.
NOTE
Be sure to create the secret in the namespace in which your application will run. Pull secrets are specific to a namespace. If you want to deploy to multiple namespaces, you need to create a secret for each one of them.
This is an example of creating a pull secret to the Azure registry. You can use the same command for any other private registry.
Shell
export DOCKER_REGISTRY_SERVER=mysampleregistry.azurecr.io
export DOCKER_USER=myregistryname
export DOCKER_PASSWORD=myregistrytoken
export DOCKER_EMAIL=YOUR_EMAIL
kubectl create secret docker-registry cfcr\
--docker-server=$DOCKER_REGISTRY_SERVER\
--docker-username=$DOCKER_USER\
--docker-password=$DOCKER_PASSWORD\
--docker-email=$DOCKER_EMAILUsing the Docker registry secret
To use the secret you just created, you need to include it, either in:
- Your pod manifests
- The service account
For Docker registry secret usage, we recommend following the official Kubernetes documentation.
Giving access to a Docker Registry via the Codefresh CLI
The Codefresh CLI can also create pull secrets in an automated manner.
See Image pull Secret.
Related articles
Kubernetes deployment quick start
Managing Kubernetes clusters